I'm always excited to take on new projects and collaborate with innovative minds.
say@niteshsynergy.com
https://www.niteshsynergy.com/
I'm always excited to take on new projects and collaborate with innovative minds.
say@niteshsynergy.com
https://www.niteshsynergy.com/
This guide explains key Spring annotations with concise descriptions and updated code snippets for practical implementation. Each section is organized by categories: Spring Core, Spring MVC, and Spring Boot, providing clarity and examples in Java and Spring Boot.
Used to define configuration classes in Spring. Equivalent to XML configuration.

Used to specify packages to scan for Spring-managed components.

Automatically injects dependencies. Can be used on constructors, fields, or setters.

Marks a class as a Spring-managed component.

Defines a Spring-managed bean directly in a configuration class.

Resolves ambiguity when multiple beans of the same type exist.

Gives higher precedence to a bean when multiple beans of the same type exist.

Injects property values into fields.

Delays bean initialization until it is first accessed.
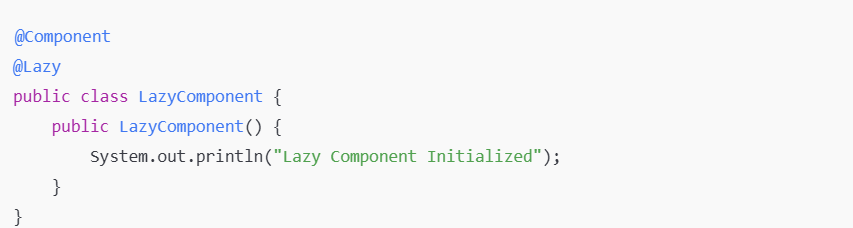
Defines the scope of a bean (singleton, prototype, etc.).

Defines profiles for conditional bean registration.
Code Example:

Indicates a class is a controller in an MVC application.

Combines @Controller and @ResponseBody for REST APIs.
Code Example:

Maps HTTP requests to handler methods.

Simplified request mappings for specific HTTP methods.
Code Example:

Handles exceptions thrown in controller methods.

Main annotation for bootstrapping Spring Boot applications.

Enables auto-configuration in Spring Boot.
Code Example:

Loads a bean based on property conditions.
Code Example:

Loads a bean if a specific class is present.
Code Example:

Marks a class as a JPA entity (mapped to a database table).
Code Example:

Specifies the database table name for an entity.
Code Example:

Marks a field as the primary key and defines its generation strategy.
Code Example:

Customizes column attributes in the database.
Code Example:

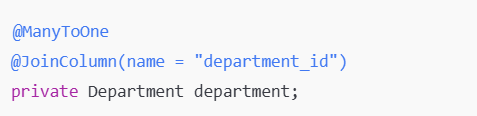
Defines relationships between entities.
Code Example (OneToMany):

Specifies the foreign key column in a relationship.
Code Example:
Used for reusable fields as embedded objects.

Defines a named JPQL query.
Code Example:
@Entity
@NamedQuery(name = "Employee.findByDepartment", query = "SELECT e FROM Employee e WHERE e.department = :department")
public class Employee {
}
Marks a class as a Spring-managed service bean.
Code Example:

Specialized @Component for persistence logic, enables exception translation.
Code Example:

A combination of @ControllerAdvice and @ResponseBody for handling exceptions in REST APIs.
Code Example:

Enables JPA repository support.
Code Example:

Ensures methods execute within a transaction context.
Code Example:

Registers a microservice as a Eureka client.
Code Example:

Enables declarative REST client for communication between services.
Code Example:

Adds client-side load balancing to a RestTemplate.
Code Example:

Handles fallback for failed service calls in Resilience4j.
Code Example:

Retries failed calls in Resilience4j.
Code Example:

Enables Hystrix Circuit Breaker in microservices.
Code Example:

Marks a microservice as a Zuul API Gateway.
Code Example:

Handles failures with fallback logic using Resilience4j.

Retries a failed request with a configurable number of attempts.
Code Example:

Limits the number of requests to prevent service overloading.
Code Example:

Isolates resources to prevent overloads.
Code Example:

Log incoming and outgoing requests at the API Gateway level.
Code Example:


Log requests and responses using GlobalFilter.
Code Example:

Enables Kafka-related configurations.

Listens to messages from a Kafka topic.
Code Example:

Used for handling multiple message types in a Kafka listener.
Code Example:

Listens for messages from RabbitMQ queues.
Code Example:

Listens for messages from ActiveMQ queues.
Code Example:

Enables Spring Security.
Code Example:
Note: **Deprecated**

Adds method-level security based on roles or expressions.
Code Example:

Simpler version of @PreAuthorize for role-based security.
Code Example:

Defines roles allowed for a method (JSR 250).
Code Example:

Enables method-level security annotations like @PreAuthorize.
Code Example:

Used in testing to mock authenticated users.
Code Example:

Marks a method as a test method.

Runs before each test method.
Code Example:

Runs after each test method.
Code Example:


Runs once before all test methods (static method).
Code Example:

Runs once after all test methods (static method).
Code Example:

Disables a test method or class.
Code Example:

Runs the same test with multiple sets of input.
Code Example:

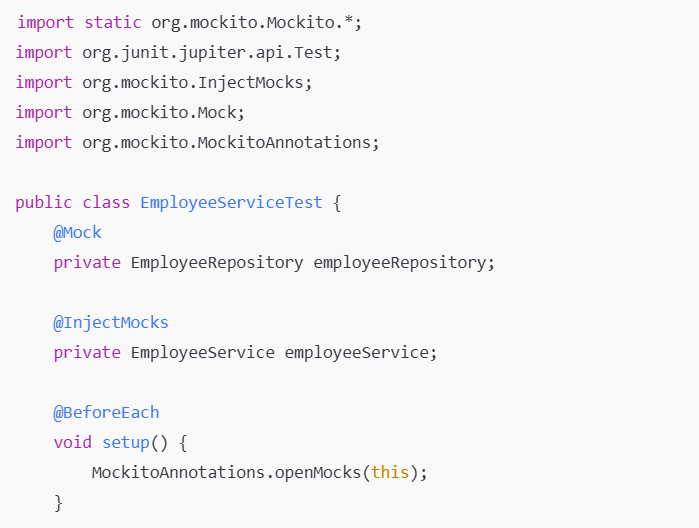
Creates a mock object.
Code Example:


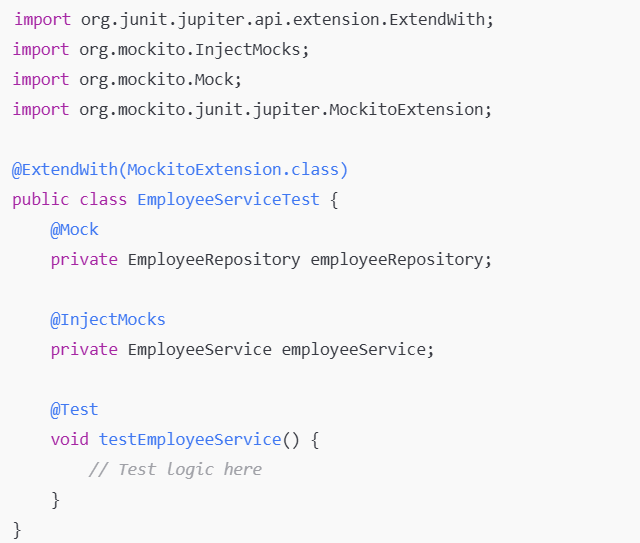
Injects mock objects into the class being tested.
Code Example:

Creates a partial mock (real methods + mock behavior).
Code Example:

Captures arguments passed to mock methods.
Code Example:


Specifies a test runner (JUnit 4).
Code Example:

Specifies a test runner (JUnit 5).
Code Example:
This annotation enables running the same test with multiple sets of input data. It works alongside various data sources like @ValueSource, @EnumSource, and @MethodSource.
Provides an array of literal values as input.
Code Example:

Provides enum constants as input.
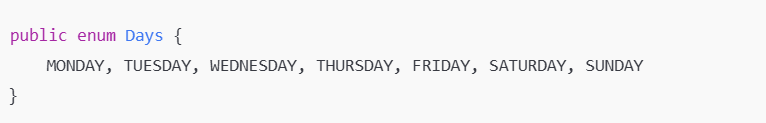

Provides test data using a static method from the same or a different class.
Code Example:


Provides input as comma-separated values.
Code Example:

Provides input from an external CSV file.
data.csv):

@MethodSource with Custom Data Classes:Code Example:



Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *